No products in the cart.
Understanding the Law of Conservation of Energy A Complete Guide
Energy is an essential aspect of our universe, governing every interaction and transformation. At the heart of this vast system lies the principle known as the Law of Conservation of Energy. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into the intricacies of this fundamental law, exploring its origins, applications, and implications for our world.
Introduction to the Law of Conservation of Energy
The Law of Conservation of Energy, often termed as the First Law of Thermodynamics, states that the total energy within a closed system remains constant over time. In simpler terms, energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only change forms. This principle revolutionized our understanding of the physical world and laid the groundwork for modern science and engineering.
Fundamental Principles of Conservation of Energy
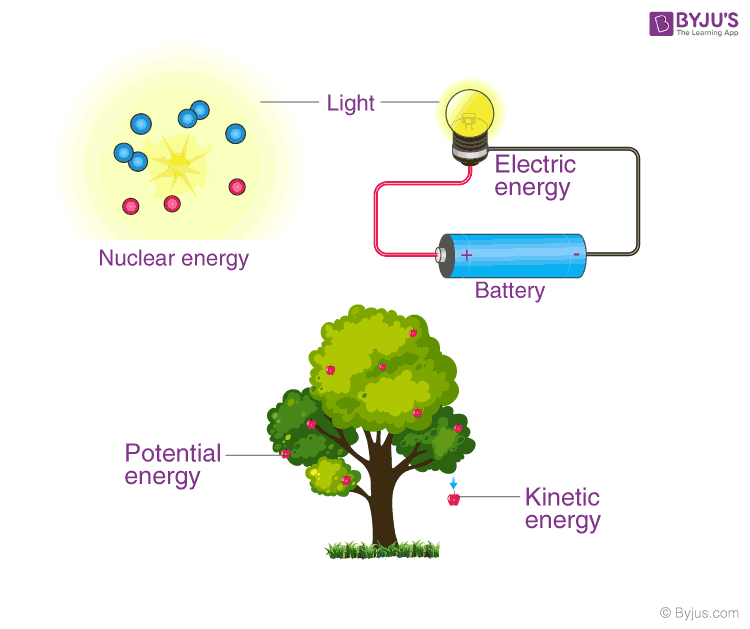
To grasp the essence of the conservation of energy, it’s crucial to understand its fundamental principles. Energy exists in various forms, including kinetic, potential, thermal, chemical, and nuclear energy. The conservation law asserts that the sum of all these energies within a system remains constant, even as they transform from one form to another.
Examples of Conservation of Energy
The conservation of energy manifests in numerous phenomena across different domains. From a swinging pendulum to a burning candle, every instance illustrates the principle at work. Whether it’s the mechanical energy of a moving object or the chemical energy released in a reaction, energy conservation governs all natural processes.
Applications of the Law of Conservation of Energy
The applications of energy conservation are far-reaching and diverse. Engineers rely on this principle to design efficient machines and systems, while environmental scientists study it to address global challenges such as climate change and resource depletion. Even in astrophysics, conservation laws play a crucial role in understanding the dynamics of celestial bodies.
Challenges to Conservation of Energy
While the law of energy conservation holds true in theory, practical applications face challenges such as friction, heat loss, and energy conversion inefficiencies. These factors introduce limitations and inefficiencies in energy systems, necessitating innovative solutions to mitigate their impact.
Einstein’s Theory of Relativity and Energy
Einstein’s famous equation, E=mc^2, introduced a groundbreaking connection between energy and mass, revealing that mass can be converted into energy and vice versa. This revolutionary concept expanded our understanding of energy conservation and opened new avenues for scientific exploration.
Real-world Implications of Conservation of Energy
The conservation of energy has significant real-world implications, especially in the context of sustainable development. By harnessing renewable energy sources and adopting energy-efficient practices, we can mitigate environmental degradation and address the looming global energy crisis.
Misconceptions Surrounding Conservation of Energy
Despite its scientific basis, the conservation of energy is often misunderstood or misrepresented in popular discourse. Myths and misconceptions abound, leading to confusion and misinformation. By debunking these misconceptions, we can foster a more accurate understanding of this crucial principle.
Importance of Understanding Conservation of Energy
Understanding the conservation of energy is paramount for individuals, societies, and policymakers alike. By optimizing energy usage and promoting conservation efforts, we can minimize waste, reduce environmental impact, and pave the way for a sustainable future.
Educational Resources for Learning Conservation of Energy
Numerous educational resources are available for those seeking to deepen their understanding of energy conservation. From textbooks and online courses to hands-on workshops and seminars, there are ample opportunities to explore this fascinating subject.
How to Teach Conservation of Energy Effectively
Educators can employ various strategies to teach conservation of energy effectively, including engaging activities, hands-on experiments, and practical demonstrations. By making the learning experience interactive and experiential, students can grasp the concepts more readily and apply them in real-world scenarios.
Future Developments in Energy Conservation
As technology advances and society evolves, new opportunities for energy conservation emerge. From innovative technologies to policy initiatives and research breakthroughs, the future holds immense potential for advancing our understanding and implementation of energy conservation strategies.
Global Efforts in Energy Conservation
Energy conservation is a global endeavor, requiring collaboration and cooperation across borders. International agreements, collaborative projects, and advocacy campaigns play a crucial role in addressing the complex challenges of energy sustainability on a planetary scale.
Challenges and Opportunities in Energy Conservation
While energy conservation presents significant challenges, it also offers tremendous opportunities for innovation and progress. By overcoming economic barriers, social resistance, and technological limitations, we can unlock new possibilities for a more sustainable and equitable future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Law of Conservation of Energy stands as a cornerstone of modern physics and engineering, shaping our understanding of the universe and guiding our efforts towards a sustainable future. By embracing the principles of energy conservation and harnessing the power of innovation, we can build a world where energy is used wisely and equitably, ensuring a brighter tomorrow for generations to come.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- Is the conservation of energy applicable only to mechanical systems?
- No, the conservation of energy applies to all systems, including chemical, nuclear, and electromagnetic systems.
- Can energy be created or destroyed?
- According to the law of conservation of energy, energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only change forms.
- How does energy conservation relate to renewable energy sources?
- Renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power rely on the principle of energy conservation to harness natural resources efficiently.
- What role does energy conservation play in addressing climate change?
- Energy conservation is crucial in mitigating climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions associated with energy production and consumption.
- Are there any limits to energy conservation?
- While the law of conservation of energy holds true in isolated systems, practical applications face limitations such as energy loss due to friction and inefficiencies in energy conversion processes.

 WhatsApp Us 24/7
WhatsApp Us 24/7